The Solubility of Gases in Ionic Liquids: A Chemoinformatic Predictive and Interpretable Approach
G.V.S.M. Carrera, J. Inês, C.E.S. Bernardes, K. Klimenko, K. Shimizu, J.N. Canongia Lopes
ChemPhysChem 2021, 22, 1-12.
Abstract
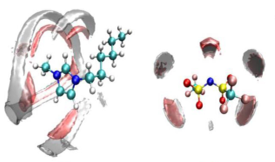
This work comprises the study of solubilities of gases in ionic liquids (ILs) using a chemoinformatic approach. It is based on the codification, of the atomic inter-component interactions, cation/gas and anion/gas, which are used to obtain a pattern of activation in a Kohonen Neural Network (MOLMAP descriptors). A robust predictive model has been obtained with the Random Forest algorithm and used the maximum proximity as a confidence measure of a given chemical system compared to the training set. The encoding method has been validated with molecular dynamics. This encoding approach is a valuable estimator of attractive/repulsive interactions of a generical chemical system IL+gas. This method has been used as a fast/visual form of identification of the reasons behind the differences observed between the solubility of CO2 and O2 in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate (BMIM PF6) at identical temperature and pressure (TP) conditions, The effect of variable cation and anion effect has been evaluated.
Return Previous Next